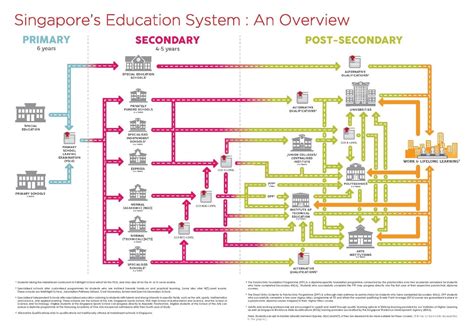
Tertiary education in Singapore is a crucial stage in the educational journey of individuals seeking to advance their knowledge and skills. It encompasses a range of post-secondary educational programmes that follow the completion of secondary school.

What are the Types of Tertiary Education Institutions?
Singapore’s tertiary education sector boasts a diverse range of institutions, each offering unique programmes and specialisations.
-
Universities
- Offer academic programmes leading to Bachelor’s, Master’s, and Doctoral degrees.
- Conduct research and contribute to advancements in various disciplines.
-
Polytechnics
- Provide vocational and professional training, leading to Diplomas, Advanced Diplomas, or Higher Diplomas.
- Focus on hands-on, industry-relevant programmes.
-
Institutes of Technical Education (ITEs)
- Provide pre-employment training and skills development, leading to NITEC (National Institute of Technical Education) qualifications.
- Cater to individuals seeking entry-level technical skills.
What are the Entry Requirements?
Admission to tertiary education institutions in Singapore is based on various factors, including academic qualifications and performance.
-
Universities
- Typically require students to have obtained the Singapore-Cambridge General Certificate of Education (GCE) Advanced Level or an equivalent qualification.
- May conduct interviews or assess portfolios as part of the selection process.
-
Polytechnics and ITEs
- Generally accept students with the GCE Ordinary Level or N(A)-Level qualifications.
- May also offer alternative pathways for individuals with relevant industry experience or prior learning.
What are the Programmes Offered?
Tertiary education institutions in Singapore offer a comprehensive range of programmes, catering to diverse interests and career aspirations.
Academic Programmes
- Arts, Humanities, and Social Sciences
- Business and Economics
- Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM)
Professional and Vocational Programmes
- Engineering
- Business and Management
- Information Technology
- Healthcare
- Hospitality and Tourism
What are the Costs?
The costs of tertiary education in Singapore vary depending on the institution and programme.
-
Government-funded institutions
- Subsidised tuition fees for Singaporean citizens and permanent residents.
-
Private institutions
- Typically charge higher tuition fees.
Financial assistance is available in the form of scholarships, grants, and loans to support students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
What are the Career Prospects?
Graduates of tertiary education institutions in Singapore enjoy excellent career prospects.
- High demand for skilled professionals in various industries.
- Graduates earn competitive salaries and have access to career advancement opportunities.
- Tertiary education provides individuals with the knowledge, skills, and networks to succeed in the global job market.
Conclusion
Tertiary education in Singapore offers individuals a pathway to advance their knowledge, skills, and career aspirations. With a diverse range of institutions and programmes to choose from, students can pursue their passions and prepare themselves for rewarding careers in the 21st-century workforce.