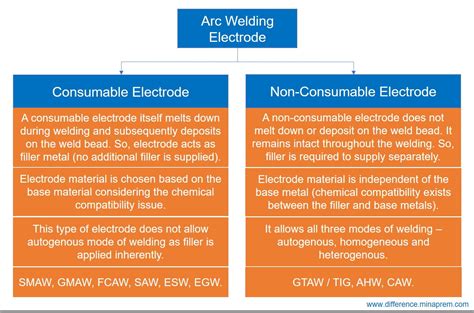
Consumable and non-consumable parts are two distinct categories of items used in various industries. Consumable parts are those that are used up or depleted over time and need to be replaced regularly. Non-consumable parts, on the other hand, are durable and can be used for an extended period without the need for replacement.

What are Consumable Parts?
Are consumable parts used up during the normal operation of a machine or device? Yes, consumable parts are components that are intended to be used once or for a limited period and then discarded. They are often essential for the proper functioning of equipment and may include items such as:
- Filters: Air, oil, and fuel filters remove contaminants and ensure the smooth operation of engines and machinery.
- Lubricants: Greases and oils reduce friction and wear, extending the lifespan of mechanical components.
- Cutting tools: Drill bits, saw blades, and milling cutters are used to shape and cut materials and need to be replaced as they become dull or damaged.
- Batteries: Disposable and rechargeable batteries provide power to electronic devices and need to be replaced when depleted.
The frequency of replacement for consumable parts depends on factors such as the operating conditions, usage patterns, and maintenance schedules. Regular replacement of consumable parts is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing equipment failures.
What are Non-Consumable Parts?
Are non-consumable parts designed to last the lifetime of a machine? Yes, non-consumable parts are components that are intended to be durable and long-lasting. They are typically made of high-quality materials and engineered to withstand repeated use and exposure to harsh conditions. Examples of non-consumable parts include:
- Structural components: Frames, housings, and covers provide support and protection for the internal components of equipment.
- Gears and bearings: These parts transmit power and reduce friction, ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of machinery.
- Electrical components: Motors, transformers, and circuit boards enable the functioning of electronic devices and systems.
- Tools and equipment: Hand tools, measuring instruments, and specialised equipment are essential for performing maintenance and repair tasks.
Non-consumable parts are usually more expensive than consumable parts, but they offer a longer lifespan and greater durability. Proper maintenance and care of non-consumable parts can extend their service life and reduce the overall cost of ownership.
Key Differences between Consumable and Non-Consumable Parts
The table below summarises the key differences between consumable and non-consumable parts:
| Feature | Consumable Parts | Non-Consumable Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | Short-term | Long-term |
| Usage | Used up and discarded | Durable and reusable |
| Replacement frequency | Regular | Infrequent or never |
| Cost | Typically less expensive | Typically more expensive |
| Examples | Filters, lubricants, batteries | Structural components, gears, electrical components |
Conclusion
Consumable and non-consumable parts play distinct roles in the operation and maintenance of equipment and machinery. Consumable parts are regularly replaced to ensure optimal performance, while non-consumable parts are designed for long-term durability. Understanding the differences between these two categories of parts is essential for effective maintenance and cost management.