What is the difference between FERA and QRA?
FERA and QRA refer to two separate concepts in engineering and management:

- FERA: Failure Effect Root Analysis
- QRA: Quantitative Risk Assessment
FERA is a technique used to identify and analyze the root causes of failures in a system. It involves examining the sequence of events leading to the failure, identifying potential failure modes, and determining the underlying causes of those failures. The purpose of FERA is to prevent or mitigate future failures by addressing the root causes.
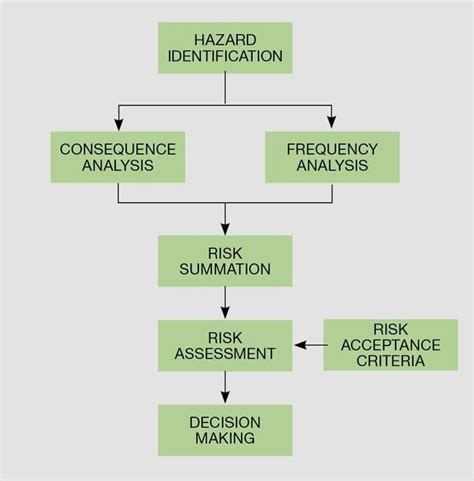
QRA is a method for assessing the likelihood and consequences of potential risks in a system. It involves identifying and quantifying the risks, estimating their probabilities and impacts, and evaluating their overall significance. The goal of QRA is to provide decision-makers with information to prioritize risk mitigation efforts and make informed decisions about risk management.
Key Differences between FERA and QRA
| Feature | FERA | QRA |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify and analyze root causes of failures | Assess likelihood and consequences of risks |
| Scope | Focuses on specific failures | Considers all potential risks |
| Methodology | Qualitative analysis | Quantitative analysis |
| Output | Root causes of failures | Risk profiles and mitigation strategies |
| Applications | Failure investigation, root cause analysis | Risk management, decision-making |
The importance of FERA and QRA depends on the specific context:
- If the focus is on understanding and preventing specific failures, FERA is more appropriate.
- If the goal is to manage overall risk and prioritize mitigation efforts, QRA is more suitable.
Both FERA and QRA are valuable tools for improving safety, reliability, and decision-making in various engineering and management domains.