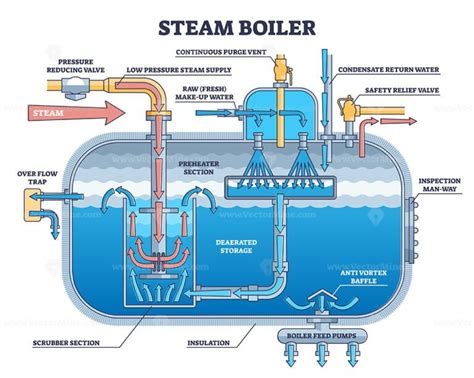
A steam boiler is a device that generates steam for industrial and commercial processes. It operates on the principle of heat transfer, converting water into steam by heating it at a specific pressure.

How Does a Steam Boiler Work?
- Water Input: Feedwater enters the boiler and flows through a series of tubes or pipes, known as the water tubes or water drum.
- Heat Addition: A heating source, such as coal, gas, or oil, heats the water tubes, transferring heat to the water inside.
- Steam Generation: As the water absorbs heat, it transforms into steam, which rises to the top of the boiler.
- Steam Separation: The steam is separated from the water in a steam drum or separator, ensuring that dry steam is produced.
- Steam Output: The dry steam exits the boiler through an outlet pipe, ready for use in various applications.
Key Components of a Steam Boiler
- Fuel source: Provides heat for steam generation.
- Water tubes or drum: Contains the water to be converted into steam.
- Heat exchanger: Transfers heat from the fuel source to the water.
- Steam drum or separator: Separates steam from water.
- Burner: Controls the combustion of fuel.
- Safety valves: Prevent excessive pressure buildup.
Types of Steam Boilers
Steam boilers come in various types, including:
- Fire-tube boilers: Hot gases flow through tubes submerged in water.
- Water-tube boilers: Water flows through tubes heated by external heat sources.
- Electric boilers: Electricity heats the water.
Applications of Steam Boilers
Steam boilers are widely used in various industries, including:
- Power generation
- Chemical processing
- Food and beverage production
- Textiles and paper manufacturing
- Healthcare and laundry facilities
Benefits of Steam Boilers
- High thermal efficiency
- Reliable and durable
- Versatile fuel options
- Low maintenance costs