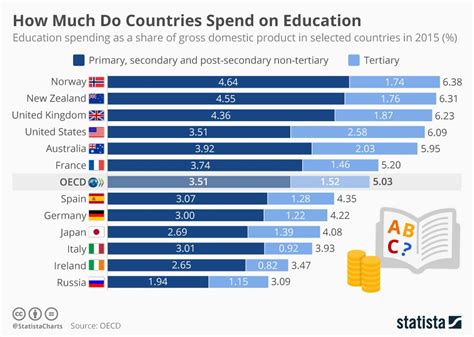
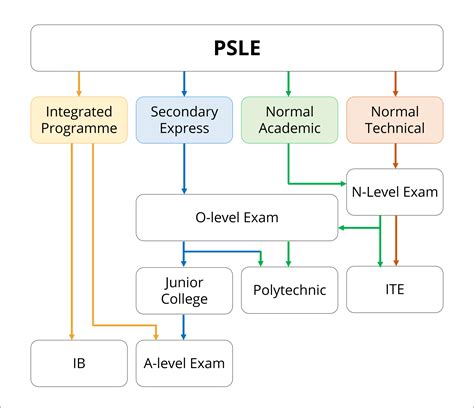
Singapore’s tertiary education rate is among the highest in the world, with over 50% of its population aged 25-34 having a university degree or diploma.

What is the Definition of a Tertiary Education?
Tertiary education generally refers to post-secondary education, including universities, polytechnics and other institutions that offer advanced or specialized training or degrees.
Tertiary Education in Singapore
Singapore places a high emphasis on education, and its tertiary education system is highly developed and diverse.
Universities
Singapore has six autonomous universities, including the National University of Singapore (NUS) and Nanyang Technological University (NTU), which are consistently ranked among the top universities in the world.
Polytechnics
Polytechnics in Singapore offer practice-oriented courses in various fields, including engineering, business, and hospitality. They play a key role in preparing students for the workforce.
Other Tertiary Institutions
Other tertiary institutions include private universities, colleges, and specialized academies that offer a range of courses in areas such as design, digital media, and healthcare.
Key Statistics on Tertiary Education in Singapore
- Over 50% of Singaporeans aged 25-34 have a tertiary qualification.
- The gross tertiary enrolment rate is over 90%, indicating the high level of participation in post-secondary education.
- Singapore’s universities are consistently ranked among the top in the world, with NUS and NTU in the top 20 in major global rankings.
- Polytechnics play a crucial role in meeting industry needs for skilled workers, with over 80% of their graduates employed within six months of graduation.
Factors Contributing to Singapore’s High Tertiary Education Rate
- Strong emphasis on education: Singapore places a cultural value on academic achievement and invests heavily in its education system.
- Skilled workforce: A high level of tertiary education is essential for Singapore’s economic competitiveness in a knowledge-based world.
- Accessible and Affordable Education: The Singapore government subsidizes the cost of university and polytechnic education, making it affordable for students.
- International recognition: Singapore’s universities and polytechnics are well-recognized internationally, attracting students from around the world.
Conclusion
Singapore’s high tertiary education rate is a testament to its commitment to providing its citizens with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in the 21st-century global economy. The diverse range of tertiary institutions and the strong emphasis on education ensure that Singaporeans have ample opportunities to pursue higher education and contribute to the nation’s progress.